"Canyon of Why"—an abyss that becomes impossible to climb out of because the loved one is never there to answer the question. Frank Campbell once said this canyon is what people who have lost a loved one to suicide often fall into. The question of "why" haunts the minds of many bereaved by suicide. While we can never really know all the reasons why people die of suicide, there are some explanations that can help us fathom how individuals might find themselves in such a state of despair.
Most people who kill themselves believe that suicide is the only solution to their unbearable situation. Sometimes the analogy of what happened in New York City on Sept. 11, 2001, gives people a framework for empathy. When one remembers Sept. 11, some traumatic images etched in memories are the pictures of people jumping out of the World Trade Center. These people did not want to die. They were leaping to get away from the flames at their back.
In a similar manner, people who contemplate suicide are trying to escape some type of peril in their own lives or unbelievable pain in their souls. Most of us find it difficult to truly appreciate the flames that consume the minds of people who contemplate suicide.
Experts who study suicide coined the term "psychache" to describe the excruciating psychological pain that people coping with suicidal intensity experience, which often blocks the ability to see other potential solutions to problems. Psychache torments individuals who often do not want to die. They just cannot escape. Even though a pervasive sense of hopelessness stifles the ability for many to seek help, most struggling with suicidal intensity feel ambivalent about taking their lives. Another common metaphor people use to describe suicidal pain is feeling trapped in a completely darkened room with no way out.
See also: New Guidelines for Preventing Suicides
A Model of Suicide Risk
In his book Why People Die by Suicide, Dr. Thomas Joiner explains that those who kill themselves not only have a desire to die, they have also learned to overcome the instinct for self-preservation. This theory goes beyond previous theories of suicide that adequately described psychological risk factors but did little to explain why some people with those risk factors died by suicide and others did not.
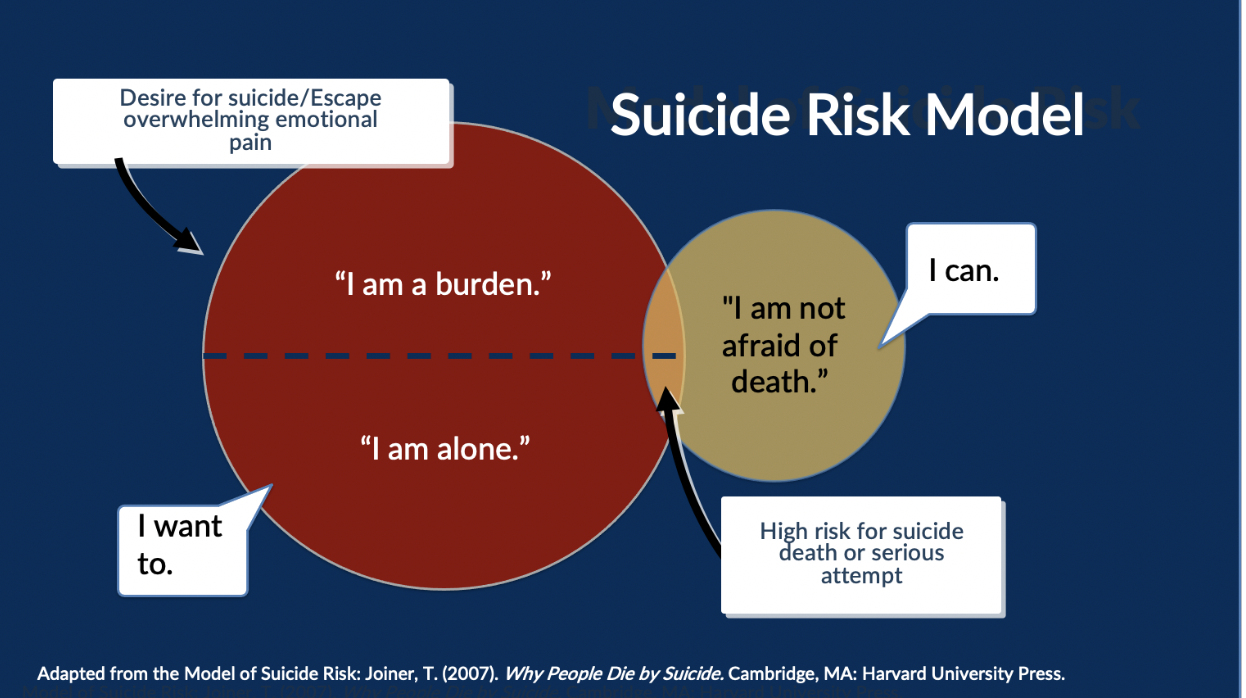
Desire to Escape Emotional Pain through Death (“I want to”)
The theory states that wanting death is composed of two psychological experiences.
"I am a burden”
The first is a perception of being a burden to others (perceived burdensomeness). According to Dr. Joiner, when people are in this state, they feel that their death is worth more to the people who love them than their life is. The word "perceived" is emphasized because frequently these thoughts are significantly distorted by depression or other mental health conditions.
While conventional wisdom might suggest the person struggling with suicidal intensity is “selfish,” Dr. Joiner has found the opposite to be true.
Those who desire suicide often believe that they have become such a burden on others, everyone will be better off if they are not around. In other words, in the mind of the person coping with suicidal intensity, they are practicing ultimate selflessness. When we combine this emotionally painful experience of being a burden with isolation, suicidal despair often results.
“I am alone”
Thus, the second common factor in the desire to die is a social disconnection to something larger than oneself (thwarted belongingness). As humans, we are hardwired to be in a relationship with others. For some people, this means just a couple of very intense relationships. For others, it means vast social networks.
When people lose key relationships with partners, children, colleagues, and friends through death, divorce, separation, moves, layoffs or conflict, they can experience profound distress that can lead to a desire to die. Marked social withdrawal is not temperamental shyness. Rather, it's a marked change: The person used to be engaged with friends and family, and now they withdraw into a bedroom or into their own head, and what you see is what Dr. Joiner calls "an inward gaze of bemused resignation and resolution."
Capability for Suicide (“I can”)
Thoughts of suicide become more lethal, however, when people have what Dr. Joiner has called a "capability for suicide." If suicide desire is the "I want to" part of the equation, "capability" is the "I can" part.
Dr. Joiner turns conventional wisdom on its head once again by challenging the notion that people who die of suicide are not cowardly. They are among our most fearless. He argues—with a lot of research behind him—that those who are most likely to take lethal action on their suicidal thoughts are those who are able to stare death down. The following three main contributing factors for capability exist:
- You are born with it. Some people just come into the world with a temperament for risk-taking. They do not seem to be afraid of anything. Natural risk-takers in our society include law enforcement personnel and military, entrepreneurs, pilots, adventure explorers, construction workers, race car drivers and emergency room doctors. These folks are not at risk for suicide unless they have the first half of the diagram, "desire to escape pain through suicide." Should that desire ever develop, however, they have less distance to cross to fatal self-harm because their fear of death or pain is not as great as in other people.
- You learn it. Other people may not be born with this sense of courage, but they learn it over time by living through painful and provocative experiences. In other words, trauma is connected to suicide. By being exposed to violence and life-and-death situations, people become more accustomed and less afraid. They have walked the path of staring death down. Trauma comes in many forms – childhood trauma, sexual trauma, military trauma. For some people, this means a history of physical abuse. For others, it is chronic injuries or illnesses that require adapting to high levels of pain. For still others, it may be repeated suicidal thoughts or attempts.
- You have access to and familiarity with lethal means. In essence, you know what to do and have confidence to do it. For example, you might have at hand firearms, lethal medications or access to high places. The more comfortable a person is with the lethal means of suicide, the more likely they will choose that method should they find themselves wanting to die by suicide.
So, in Dr. Joiner's theory, we must have both conditions to have increased risk for suicide. A desire for suicide is necessary but not sufficient. As mentioned earlier, thoughts of suicide are relatively common, but suicide death is much less so. This is because most people who have suicidal thoughts, thankfully, do not have the capability for lethal self-harm.
See also: 10 Tips for Preventing Workplace Suicide
Suicide in Context
Understanding the suicidal person from a mental health perspective limits our understanding. Suicide needs to be seen in a larger context within the cultures people belong to – in other words, there are also social determinants to suicide.
For instance:
- Discrimination/Prejudice/Exclusion
- Bullying/Harassment/Hazing/Toxic workplaces
- Exposure to trauma
- Family violence
Many now question the highly medicalized framework of understanding a suicidal person and see suicide in context by understanding how other frameworks — like social justice — expand our imagination on what is possible in prevention, intervention and "postvention."
Many traditional efforts in suicide prevention have failed us, including:
- Forced treatment
- Fear-based approaches of restraint and isolation
- Trying to predict suicide risk
Instead, explore alternative, environmental-based approaches. It’s not good enough to send “troubled” people to counseling; we must also look at fixing the toxicity in our environments that drive people to despair.
Conclusion
As researchers ask questions to those most directly affected by the crisis of suicide—both those struggling with suicidal intensity and those left behind—the mystery of suicide becomes less of an enigma and more of a significant preventable public health problem. That problem is one that we need to address at the individual level, at the organizational level and at the cultural level.








