AI adoption in the insurance industry is gaining traction. According to Earnix's recent Industry Trends Report, 70% of insurance executives plan to implement AI models that use real-time data predictions within the next two years — more than double today's adoption rate. It's clear that insurers are increasingly relying on real-time predictive analytics as AI adoption accelerates.
As AI technology advances within the industry, insurers are leveraging both traditional AI, which analyzes data and predicts outcomes, and generative AI, which creates content and explains concepts. As they adopt these technologies, insurers can expect significant improvements across operations.
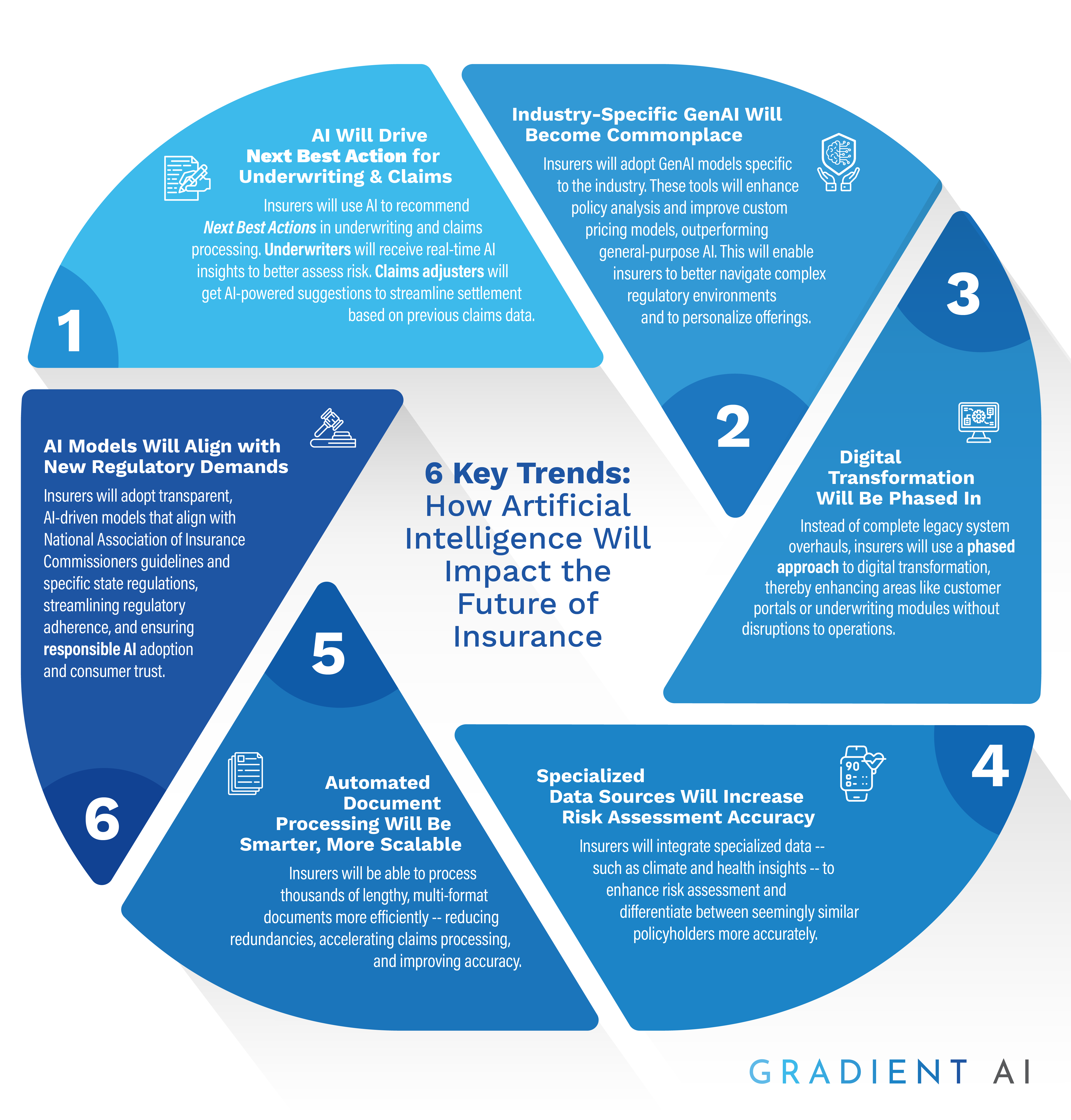
Here are six trends shaping the future of AI in insurance.
1. AI-Powered Next Best Actions for Underwriting and Claims
Currently, insurers use AI for tasks like processing straightforward data inputs or automatically categorizing claims. In the future, insurers will also leverage AI to provide next best action recommendations for both underwriting and claims management.
"Next best action" recommendations will provide underwriters with specific suggestions such as adjusting coverage limits or gathering additional data sources to better assess risk, based on AI-driven insights. Similarly, for claims adjusters, AI will suggest next best actions such as seeking out additional documentation or identifying an optimal settlement path based on previous claims data. By automating complex decision-making, AI enhances efficiency, consistency, and speed across underwriting and claims operations.
2. Industry-Specific GenAI for Insurance
While many insurance companies have experimented with general generative AI tools, these often fall short when it comes to the industry-specific needs of insurers, like analyzing policy language or understanding regulatory requirements.
As demand grows, insurers will increasingly adopt specialized GenAI models designed specifically for the insurance sector. These advanced tools efficiently interpret intricate policy documents, generate custom pricing models, and draft precise policy language, far beyond the capabilities of general models. This shift enables insurers to better navigate complex regulatory environments and improve their ability to design personalized insurance products, ultimately leading to greater accuracy and customer satisfaction. As technology evolves, insurers will increasingly rely on these specialized solutions to enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and deliver more customized coverage for policyholders.
3. Phased Digital Transformation
Nearly half (49%) of insurers report falling behind in updating legacy systems, according to Earnix's report. While many insurers have attempted to modernize their legacy systems, these efforts often fail due to their complexity and scope. Replacing all core systems at once often overwhelms insurers, leading to costly setbacks.
In the future, insurers will increasingly rely on a phased approach to digital transformation, implementing targeted upgrades instead of complete system overhauls. This approach allows companies to focus on specific areas like customer portals or underwriting modules, integrating AI gradually and minimizing disruption to existing operations. This incremental strategy helps insurers avoid the pitfalls of past modernization attempts while still improving efficiency and competitiveness in the market. The key is to focus on smaller, high-impact projects that deliver immediate value, driving change and building momentum over time.
4. Specialized Data Sources for Smarter Risk Assessment
Insurers today typically rely on broad data sets like historical loss data, demographic information, and general weather reports to assess risk.
In the future, we will see AI models that incorporate more specialized data sources to improve the accuracy of risk assessments. For example, insurers may use climate change information from coastal surveillance or community-based environmental organizations to better assess property or health risks. Health insurers may leverage fitness-related information from smartwatches to differentiate between policyholders who may look the same in a policy application but actually represent vastly different risk profiles (e.g., active triathletes vs. sedentary individuals with significant latent health risks). By integrating precise data into their models, insurers gain a holistic view that enhances risk assessment and policy pricing accuracy.
5. Smarter, Scalable Document Processing
Currently, many insurers use basic document automation for tasks like summarizing brief records or extracting information from structured documents. However, processing large, complex files like medical records still requires significant manual input.
In the future, AI-driven document processing will change how insurers manage documents at scale. Insurers will be able to process thousands of lengthy, multi-format documents efficiently, handling everything from de-duplicating redundant data to categorizing unstructured records. For example, AI will swiftly summarize and organize critical information, eliminating time-consuming, manual reviews for complex claims. This means that claims processing will be faster and more accurate, allowing insurers to manage even higher volumes of claims while reducing error rates and improving customer satisfaction.
6. AI Models That Align With New Regulatory Demands
As insurers expand their use of AI to streamline underwriting and claims management, industry standards for responsible AI use are becoming more uniform across states. Recently, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) adopted a model bulletin outlining compliance requirements for insurers' AI systems. This bulletin clarifies expectations for development, deployment, and documentation of AI technologies to ensure adherence to state and federal laws. So far, at least 11 states, along with Washington, D.C., have issued bulletins incorporating NAIC's language. They are: Alaska, Connecticut, Illinois, Kentucky, Maryland, Nevada, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Washington.
This year, expect to see insurers adopt transparent, AI-driven models that align with both NAIC guidelines and specific state regulations. These models include explainable AI components to ensure clear, auditable insights into predictive processes to meet compliance demands. For insurers operating across state lines, these advancements streamline regulatory adherence and enhance consumer trust by offering transparent, ethical risk assessments. This shift establishes responsible AI use as a foundational standard in the industry.
AI is now an integral part of the insurance industry, helping insurers streamline operations, enhance processes, and navigate regulatory requirements. As its role expands, so does its value, providing deeper insights that support better business decisions. The future of insurance will depend on how effectively companies adopt AI to meet evolving expectations while building customer trust and confidence.