Insurers lose billions annually due to unprecedented fraud. This article examines insurance fraud detection, comparing AI and human experts and showing how they can combine to improve the insurance industry.
Insurance Fraud Detection Challenges
Insurers struggle to detect and prevent fraud due to its variety. Some common types of fraud are:
- People stage accidents to file fraudulent insurance claims.
- People overstate damage.
- Identity thieves file fake claims using real policyholders' information.
- Doctors send fake bills to insurance companies.
Due to the volume and complexity of fraudulent claims, insurers struggle to detect and prevent fraud manually.
AI and Machine Learning: A Solution for Insurance Fraud Detection
AI and machine learning systems can analyze massive data sets to find fraud trends and even detect and prevent fraud in real time. However, using AI and machine learning to detect fraud is difficult. The biggest obstacles are:
- Low data quality: The quality of data strongly affects AI and the accuracy of machine learning algorithms. Insurers must ensure accurate, complete and up-to-date data for optimal results.
- Bias: AI and machine learning systems can exhibit favoritism toward specific claims or individuals, leading to erroneous or unjust outcomes. Insurance companies have a responsibility to guarantee that their algorithms are unbiased.
- Privacy: AI and machine learning for insurance fraud detection raise privacy concerns because sensitive personal data may be evaluated. Insurers must follow data privacy laws to protect client privacy.
Despite these drawbacks, AI and machine learning for fraud detection have many benefits, including:
- Speed and accuracy: AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze massive amounts of data in real time, detecting fraud and clearing the handling of legitimate claims.
- Cost savings: Insurance companies can save billions of dollars in reimbursements and other expenses.
AI still requires human oversight to ensure accuracy and dependability, and it will likely continue to require such oversight.
The ability of artificial intelligence to detect fraud is hindered by both false positives and false negatives. These errors may occur if the AI algorithms are not calibrated properly or if they are based on data that is either incomplete or inaccurate. Another possibility is that the data used to train the algorithms is incorrect. Human oversight is needed.
Investigation and resolution of suspicious transactions are another important role for human oversight. AI is able to recognize patterns and anomalies that may point to fraudulent activity, but it is still up to humans to investigate and determine whether they are.
The following table shows the key differences between AI and human investigators.
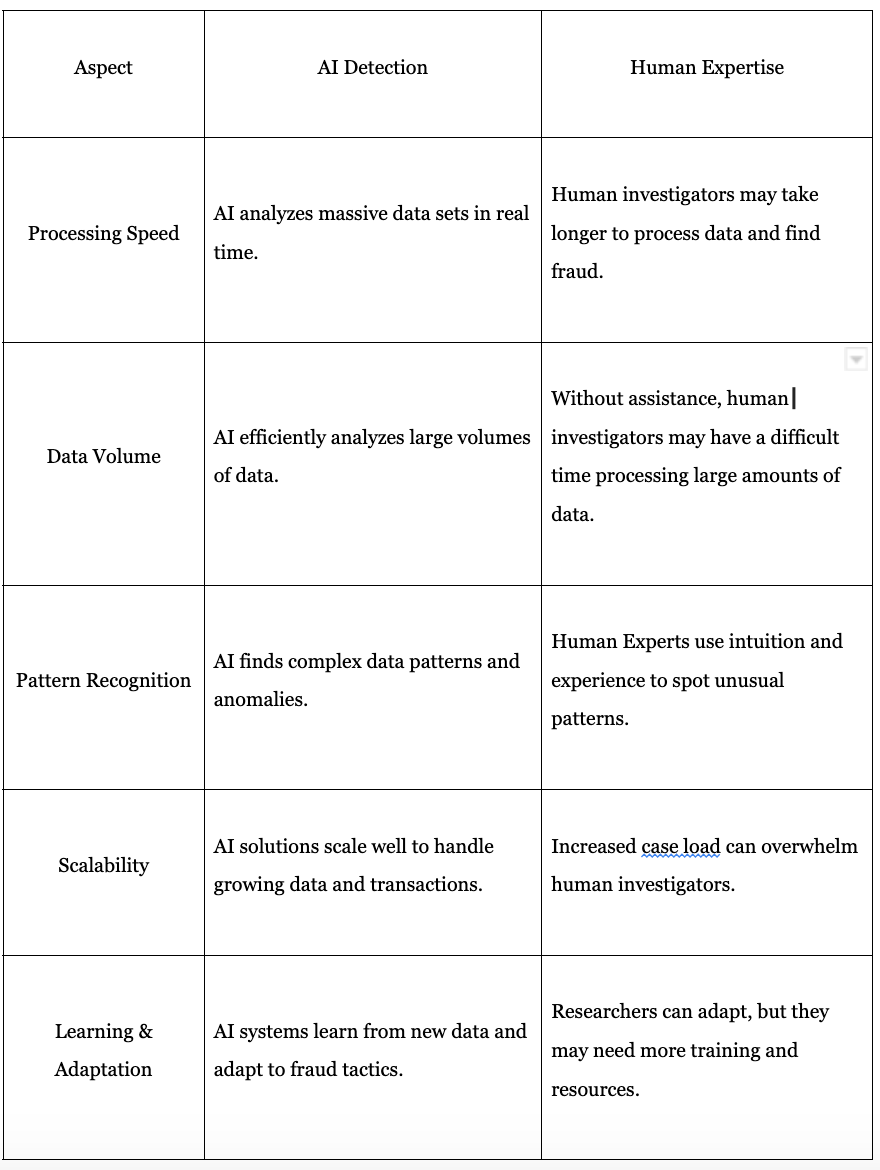
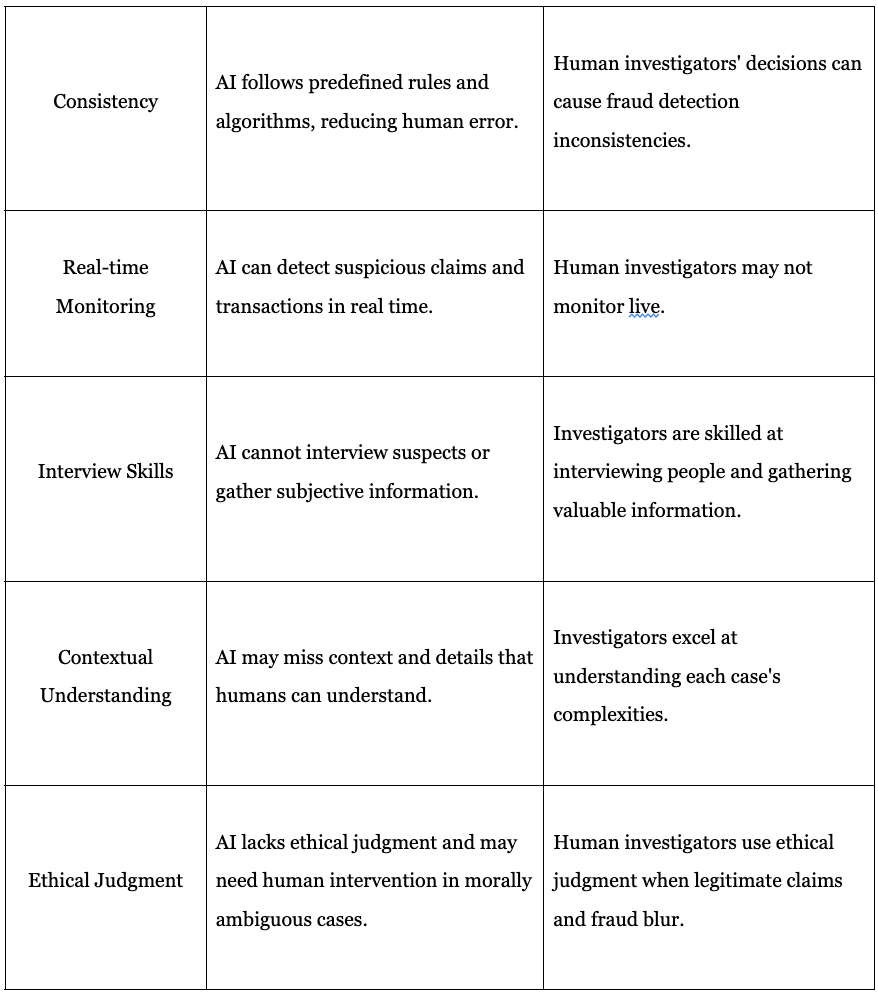
AI is a powerful ally against insurance fraud. But, while AI can quickly analyze data, human oversight is essential for accuracy.






