As inflation and increasing global risk push up the cost of coverage, a powerful tool has gained traction in recent years: partial or total self-funding of workers' compensation.
While companies assume more risk, they get significantly more control over coverage, claims management and associated costs. The result is often highly cost-effective.
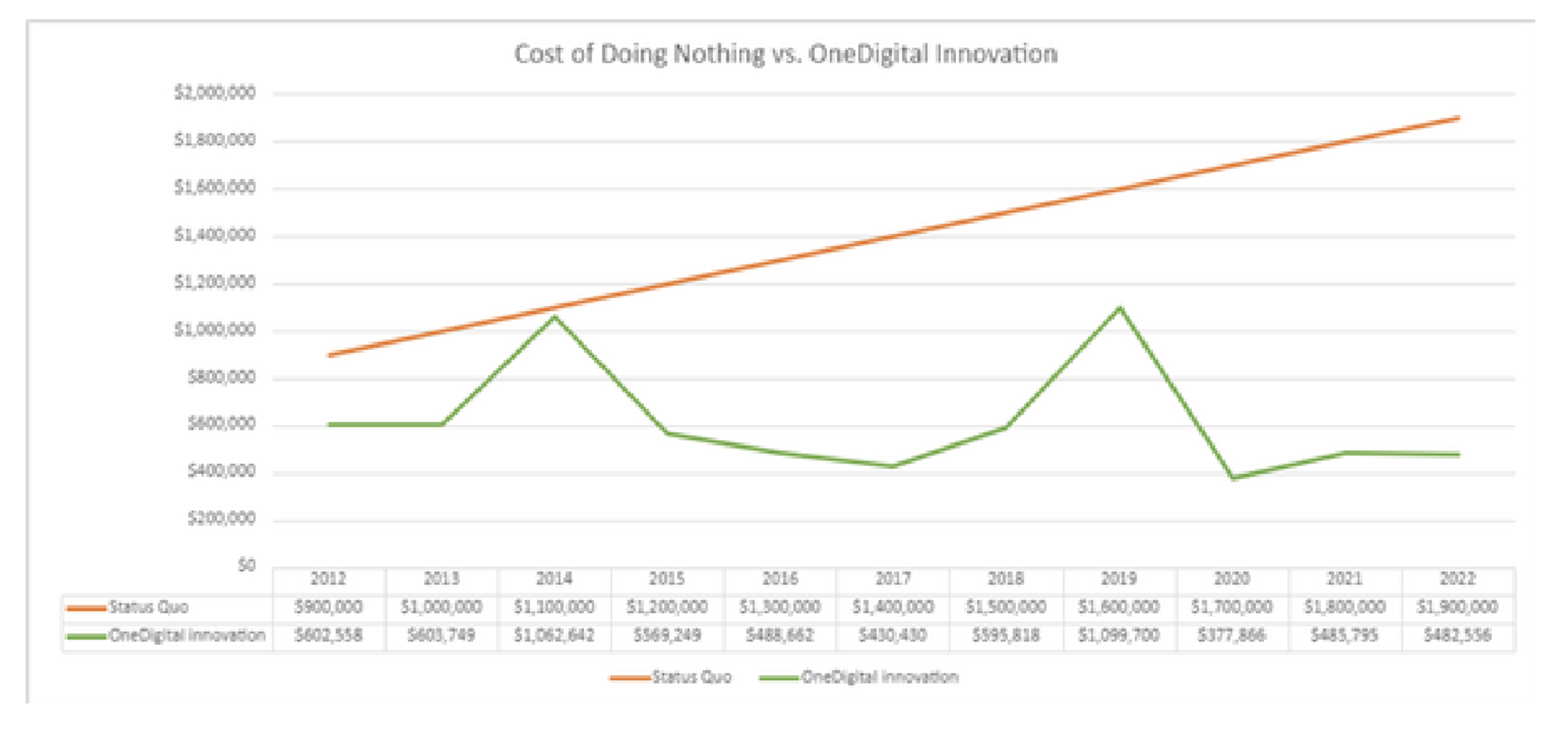
For example, when OneDigital client Wheeler Health, a healthcare and human services provider, was grappling with an increase in its workers’ compensation premiums, the answer came in the form of a partially self-funded plan. This program did two things for Wheeler Health: It helped manage the financial burden (workers' compensation expenses had soared to nearly $1 million for a $25 million payroll) and gave the client a more active role in claims management.
The plan leveraged an A+ national insurance carrier without the need for unconventional claims-handling methods or a third-party administrator and offered a smooth transition – claims reporting continued as usual to the insurance carrier, with fixed monthly premiums. The fixed-rate premium increased less than 2% annually.
Savings have run into the millions of dollars over the past decade. Had Wheeler remained on their fully insured plan, their annual workers’ compensation costs would hover around $1.8 million to $2 million.
Partially self-funded workers' compensation programs offer greater financial control and cash management by allowing companies to only pay for actual, incurred claim expenses, reducing the need for fully valued traditional insurance premiums. This approach fosters a stronger safety culture, as companies see precisely where their premium dollars are going and become more invested in preventing workplace accidents and injuries to minimize claims and costs.
By tailoring their self-funded plans, companies can align workers' compensation strategies with industry-specific needs and risk profiles, optimizing coverage and cost-effectiveness. This transformative model can also greatly enhance employee well-being and productivity and overall organizational resilience.
See also: Case Study on Using AI in Workers' Comp
Why Don’t All Groups Take Advantage?
While the financial benefits of well-designed partial or fully self-funded workers' compensation plans are extraordinary, they aren't that common. Some possible reasons are a general lack of understanding and limited product knowledge. Quite frankly, it’s also less profitable for insurance companies when clients move to this type of plan.
But, as you can see, the benefits can be substantial.
 Employers with a substantial payroll, a strong commitment to workplace safety and a desire to reduce workers' compensation expenses should consider this option.
Employers with a substantial payroll, a strong commitment to workplace safety and a desire to reduce workers' compensation expenses should consider this option.






