Rapid technological advances and changing customer behaviors have accelerated change in many industries. COVID-19 has accentuated the pace of disruption. Insurance companies need to be ready to face these new challenges and take advantage of opportunities.
Insurers have always been data-savvy, but they will have to move faster than ever to keep pace with competitors and other industries. Given the higher volume and velocity, insurers must invest further in their capabilities to store and compute their data assets.
The journey begins with solving for data silos that have been created over decades and that inhibit Insurers. The presence of multiple legacy systems may elongate the transformation, so insurers must use automation to achieve speed to value and reduce costs.
Below are the key business imperatives that a modern-day insurer needs to enable to stay ahead of competitors.
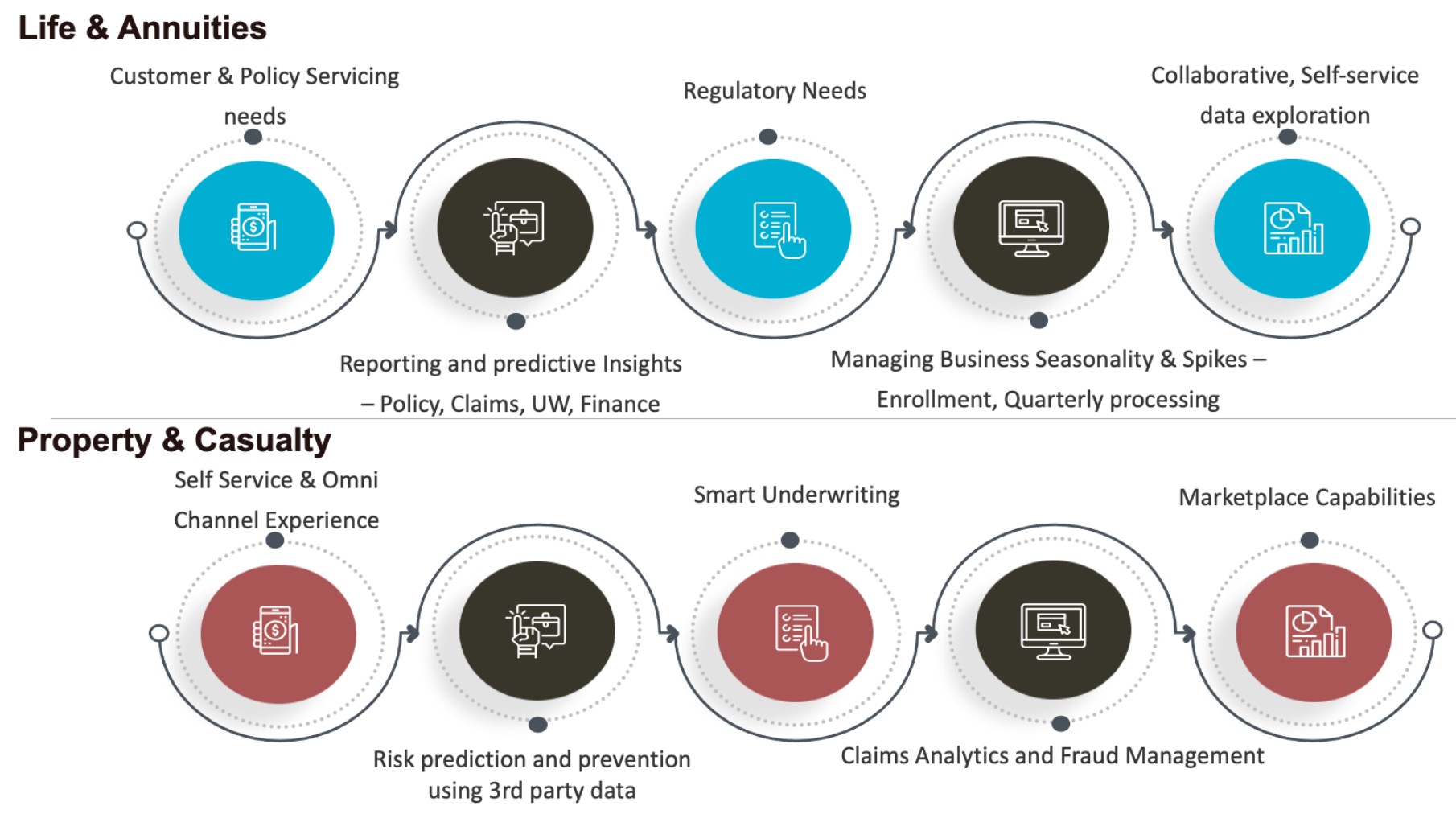
The insurance sector of the future will look very different, and this shift has already started to happen across the value chain. Insurers are increasingly re-shaping their roles and value propositions, transforming from purely insuring risks to being data-driven and value-based.
"Data on Cloud" is the driving force behind much of this change and presents a solution for Insurers.
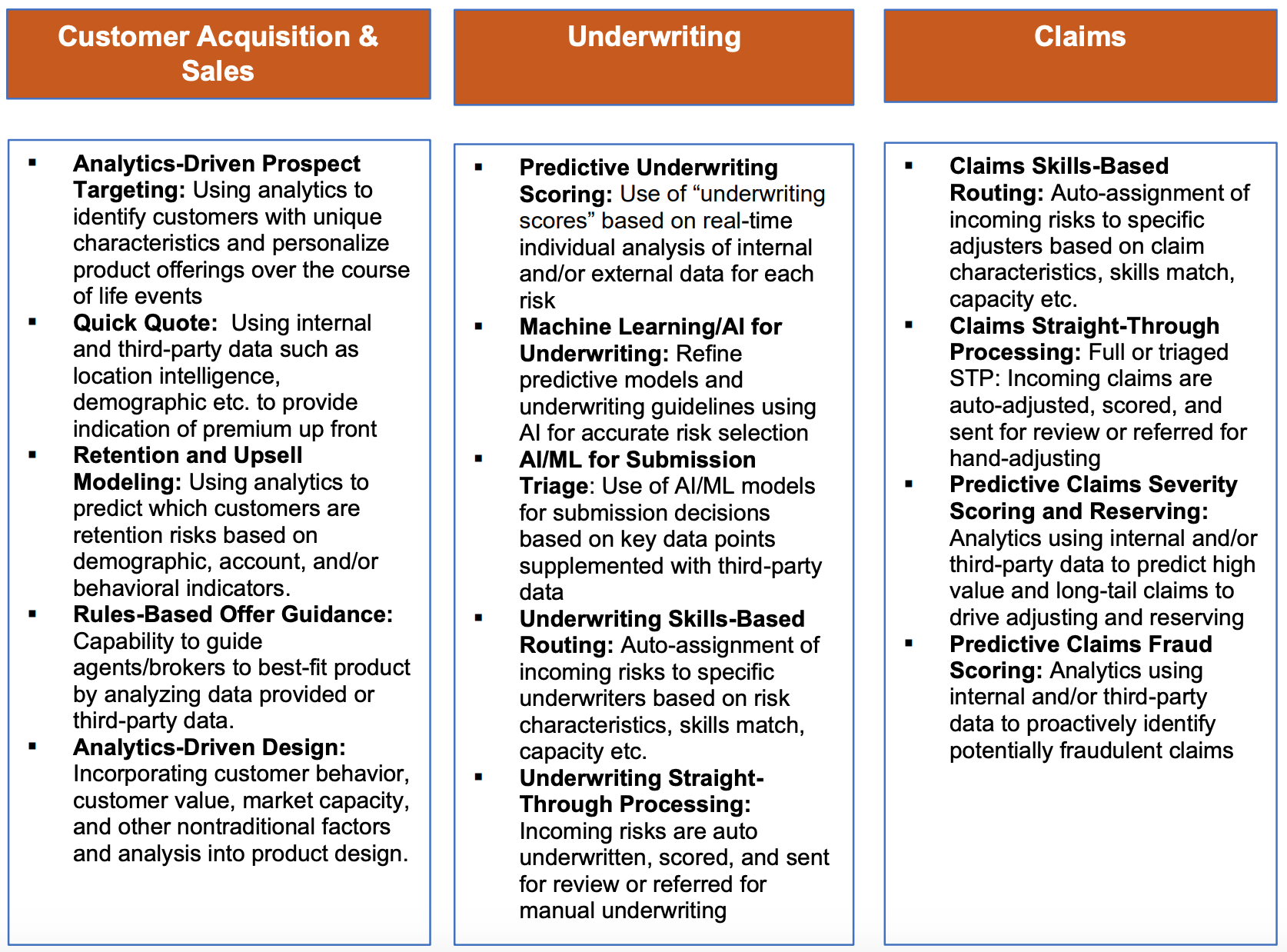
Opportunities for data-driven insurers
For insurers that are weaponizing data, there are tremendous opportunities. Here are key use cases that can be enabled:
See also: Thinking Big for True Transformation
Key decisions that affect the data cloud strategy
Here is a way to envision those decisions:
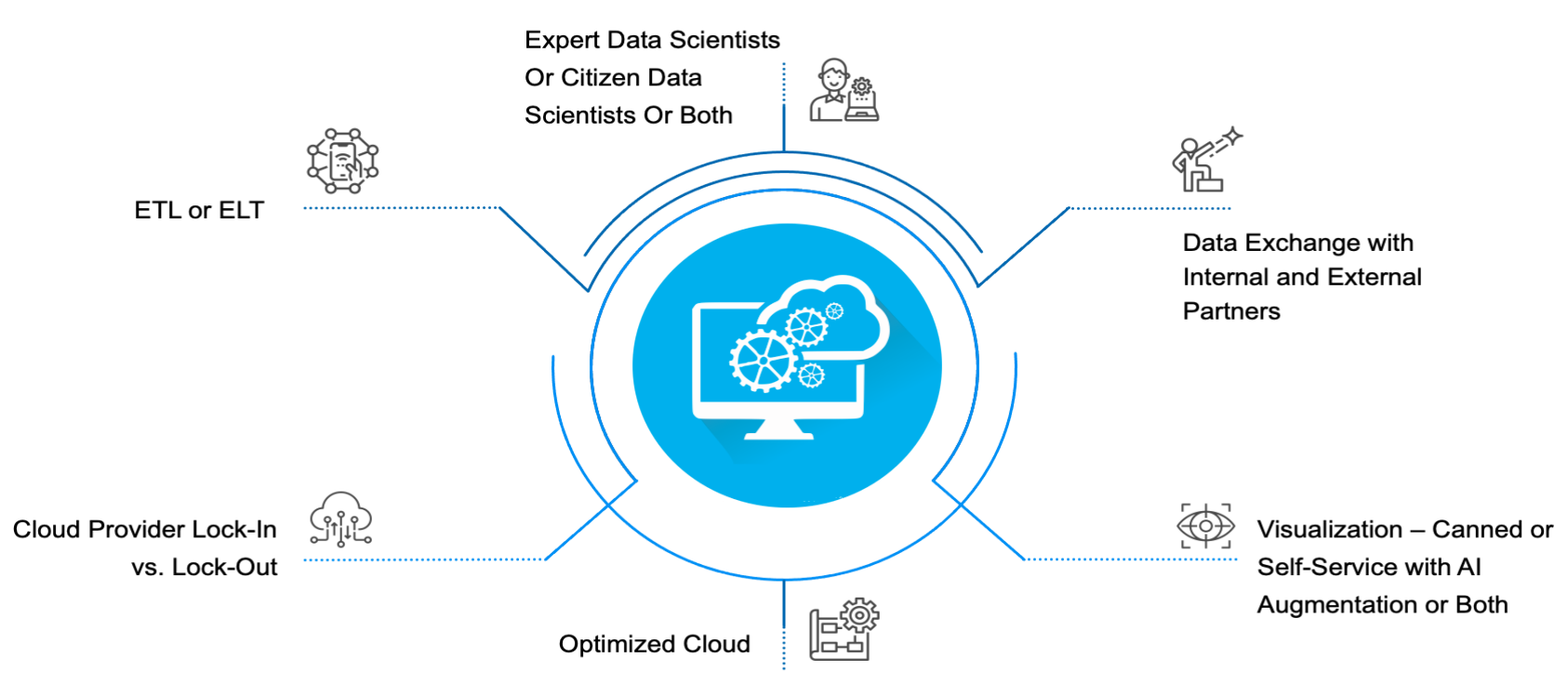
Key Decision: Cloud provider lock-in vs. lockout
Recommendation:
All public cloud providers are continuously enhancing their capabilities to keep up with customer needs. While most key capabilities are common, each cloud provider brings in a few unique capabilities. That’s why it is prudent for Insurance enterprises not to get locked in to one public cloud provider and be flexible.
Evaluate available options against each architectural building block and pick the best available across the cloud platforms -- perhaps Snowflake for cloud data platform and Azure Synapse or AWS S3 for your data lake needs, especially around unstructured data.
Key Decision: ETL or ELT?
Recommendation:
ETL – Extract, Transform and Load is used mostly in traditional architectures. As the ETL engine needs to transform a large amount of data, it usually hosts a complex logic and is expensive to run and maintain.
ELT – Extract, Load and Transform is more suitable for cloud-based data platforms. It is about scaling and processing data in parallel without any impact on performance. A cloud data warehouse such as Snowflake separates storage from computing and allows both to scale as needed. This is especially cost-effective when you consider the amount of resource required to transform data in legacy systems before loading it.
Key Decision: Expert vs. citizen data scientists or both?
Recommendation: Every enterprise has different needs when it comes to AI/ML capabilities, although most insurance enterprises are looking to enable citizen data scientists’ capabilities in addition to expert data scientists, to achieve the scale and speed that the organization needs. While enabling key features around model building and operationalizing, such as notebook, "API-ification" of a model, model refresh and release to production, the data platform must also be able to support the compute and storage needs for data science use cases. Snowflake's key feature of isolated loads provides separate computing power for each use case, and Auto scales up or down based on data processing volumes.
Key Decision: Data exchange vs. sharing
Recommendation: One of the key needs for building a true data culture is to enable smooth exchange and sharing of data sets. Datasets that are certified by one team can be used by other teams within the enterprise without spending time on the data prep and cleansing work. This facilitates faster insight generation while increasing accuracy. Third-party data plays a critical role in insurance, so, having a streamlined mechanism to procure, certify and publish third-party data is critical. Many insurers are setting up private a data marketplace to facilitate sharing, smooth integration with third-party data and centralized cost monitoring. Although most public cloud providers come with their own marketplace, Snowflake is a step ahead in this capability because of industry-specific data sets and seamless integration with Insurance core systems using APIs.
Key Decision: Visualization with self-service and AI augmentation
Recommendation: Business intelligence (BI), visualization and analysis ultimately decide how successful your data initiatives are. Technologies such as augmented analytics combine machine learning and AI to assist data preparation, insight generation and explanation to augment how people explore and analyze data in analytics and BI platforms. Adding the power of natural language processing with data for faster and accurate diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive algorithms, we can empower business users to interact with data more effectively.
Key Decision: Optimized cloud
Recommendation: Success of data on a cloud platform does not only depend on building it right but also on how well it is optimized to run post-implementation for cost, performance and security. It is important to have the right governance in place to avoid sticker shock. Most cloud platforms provide some ways of monitoring, but having a solution customized to your organization is critical.
See also: 20 Insurance Issues to Watch in 2022
Why "Data on Cloud"?
Insurers need to think long-term while choosing a data platform, so it is recommended that they choose cloud-agnostic capabilities that are scalable, secure and at the same time very cost-effective. Generally, SaaS-based offerings can go a long way because they provide near-zero maintenance cost while providing enough flexibility to configure, manage and govern the data platform based on the specific needs of each insurer.
In summary, the recommendations are:
- Separate Computing and Storage — providing the ability to have unlimited computing power for isolated workloads while not worrying about storage costs.
- Auto Scaling — providing auto scale-up and scale-down based on data workloads, without manual intervention or any process delays.
- Third Party Data Exchange — providing seamless data integration with third-party data sources, whether through a marketplace or an API-enabled mechanism.
- Data Sharing — providing the ability to share data with internal and external stakeholders with the right access control mechanisms.
- Data Integration — working with various tool sets, including cloud native connectors to integrate data from a variety of sources, such as core insurance products, mainframes, IOT and telematics.







