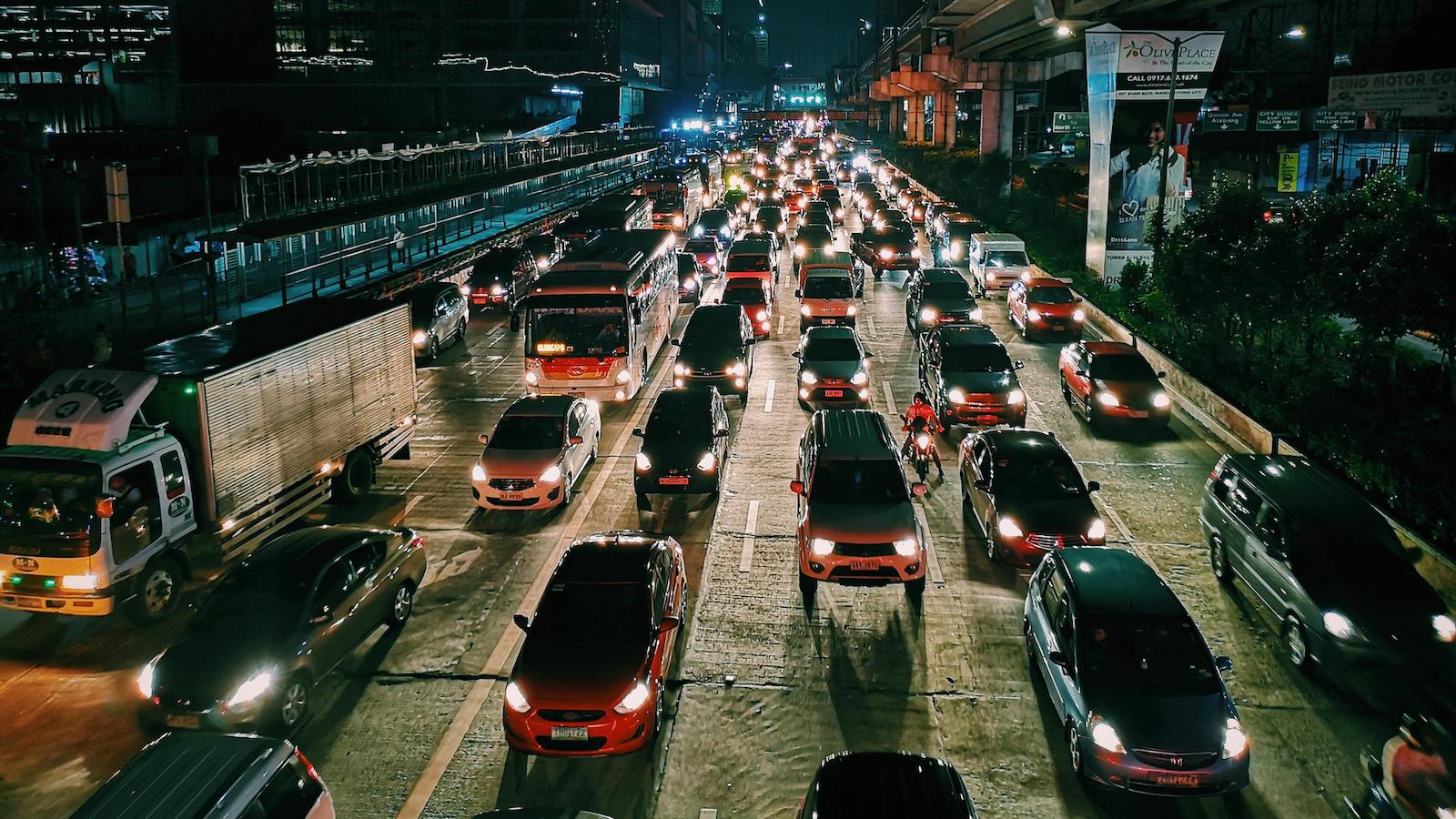
We're standing at an exciting juncture where road safety, auto insurance and technology converge. AI isn't just an added feature; it's transforming the very fabric of mobility and insurance. It allows us to reimagine risk assessment to be granular and precise by tapping into vast amounts of real-time data from vehicles using telematics and computer vision.
Insurance is no longer a one-size-fits-all proposition; it's personalized. Data on driving habits, distances traveled and even the time of day now determines insurance premiums. This not only encourages safer driving but also provides a tangible route to transparent and accurate risk assessment, for fairer underwriting.
We’re not just assessing risk in hindsight but foreseeing and mitigating it. For starters, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, or ADAS, and computer vision are going beyond warning drivers of impending collisions and are preventing them. These systems are building up to fully autonomous driving.
See also: How Geospatial Data Lowers Traffic Risk
Driving Force Behind Safer Roads
Computer vision as a technology is capable of mechanically "seeing" and understanding the details of visual information. Using in-car cameras that provide real-time alerts for driver distraction and potential collisions, these integrated features direct safer driving practices. Imagine significantly reducing human error, which accounts for over 90% of traffic accidents. That's what AI brings to the table.
AI-powered telematics devices contribute to road safety by monitoring driver behavior, vehicle performance and environmental factors in real time. By analyzing this data, AI can predict potential hazards and provide warnings to drivers. These insights can be used for coaching drivers toward safer driving habits, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
ADAS improves both driving experience and safety by using sophisticated sensors and cameras to assist drivers. Features such as automatic braking, lane-keeping assistance and adaptive cruise control help mitigate human errors, providing a buffer against accidents. ADAS can take immediate action in critical situations faster than a human might react, thus averting potential collisions.
AI telematics, computer vision and ADAS together deliver complementary benefits for reducing road incidents and creating a comprehensive safety net. While computer vision and telematics focuses on monitoring, analyzing and improving driver behavior over time, ADAS provides immediate interventions to prevent accidents.
Tailoring Risk to Real Behavior
Analyzing vast and real-time vehicular data sets provides a comprehensive profile of driving behavior, driver history and usage patterns, to deliver fair and accurate risk assessment. AI algorithms trained on millions of use cases can detect patterns for fraud detection, analyze data to forecast future events and assess the likelihood of various outcomes. AI helps build personalized, accurate and tailor-made insurance products that can integrate seamlessly with existing solutions and deliver an enhanced customer experience.
AI has also been a game-changer in streamlining claims processing. Consider a scenario where, instead of waiting for an appraiser or adjuster, a driver can simply take images of their damaged vehicle after an accident. These images are then processed by AI, which not only appraises the damage but also verifies the nature of the claim. This translates to faster response times, quicker settlements, fraud reduction and enhanced accuracy—all leading to a swift, safe and fair settlement experience.
Data-Driven Safety
AI is not just a technological leap but also a collective stride toward a wider socio-economic impact. With safer drivers on the road, we can hope for reduced accidents, lesser claims and reduced pressures on healthcare systems. Beyond the fiscal implications, there's an intrinsic human value in potentially saving lives and in the peace of mind brought about by a safer environment.
Telematics and computer vision, in today’s mobility ecosystem, are key drivers of this change. The rapid adoption of connected vehicles—be it EVs or hybrids—is not just transforming the automotive world but also propelling AI and insurance industries forward.
This connectivity enables the collection of vast data sets, to create personalized and efficient insurance solutions. This data-rich environment will further encourage safer driving behaviors, aligning insurance premiums with real-time driving patterns and engendering a culture steeped in responsible driving and road safety.
See also: Auto Claims and Collision Repair: The Great Reset
The Future With AI at the Wheel
As we stride confidently into the future, a robust, forward-thinking regulatory framework is essential to navigate these complexities, ensuring AI technologies not only push the boundaries of what's possible but do so responsibly and transparently. AI systems often rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively. Compliance with data protection and privacy to safeguard users' data will enable greater acceptance and adoption of AI technologies.
The future holds a connected sphere where cars communicate seamlessly. Business innovation will then center on vehicle identity, in-car payments and diverse in-vehicle services that will reshape the insurance business models, while promising a safe, more secure and sustainable future for mobility.